Isobutanol: The price difference with n-butanol continues to widen, and is expected to gradually narrow in the future.
【Introduction】 In recent years, isobutanol and its related product n-butanol have shown a high degree of price synchronization, but the price drop of n-butanol has been far greater than that of isobutanol. Since 2024, the price difference between isobutanol and n-butanol has been widening. With the concentrated commissioning of a new round of new production capacity, the future supply and demand pattern of the two will undergo drastic changes, and the price difference between isobutanol and n-butanol is expected to quickly return to normal.
Since 2025, the domestic isobutanol market has generally shown a trend of rising first and then falling, and the price of n-butanol during the same period is similar to that of isobutanol. In contrast, except for January, isobutanol prices have been significantly higher than n-butanol prices for most of the remaining time, continuing the high price difference characteristic since the second half of 2024. According to data monitored by Zhuochuang Information, as of the close of May 23, the price of isobutanol in Jiangsu from January to May 2025 was 7592 yuan/ton, while the price of n-butanol during the same period was only 6908 yuan/ton, with a price difference of 684 yuan/ton.
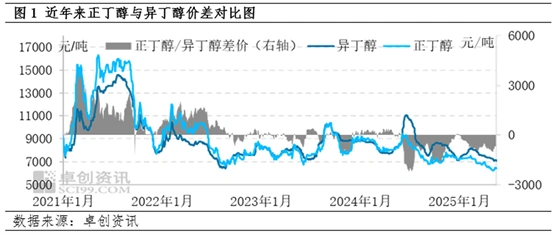
In the long run, the price of isobutanol is significantly lower than that of n-butanol, which is strongly related to the pricing mechanism of isobutanol. After 2024, a new change occurred in the price difference between the two, and for a period of time, isobutanol was significantly higher than n-butanol. During 2024-2025, the price difference between the two once widened to 600-1500 yuan/ton, showing a strong deviation from historical data, which is closely related to changes in product fundamentals.
The widening price difference between isobutanol and n-butanol is closely related to the rapid decline in n-butanol prices.
In the past five years, the price of n-butanol has shown a trend of rising first and then falling. Taking the Jiangsu market as an example, the highest price of n-butanol appeared in 2021, at 16300 yuan/ton; the lowest point appeared in 2025, at 6200 yuan/ton, with a price difference of over 10000 yuan/ton. The drastic changes in the price of n-butanol are closely related to its own fundamental data, especially after the high-profit-driven expansion of a new round of production capacity, the supply structure has transitioned from a previously tight balance to an oversupply, resulting in a significant decline in prices and profits.
In contrast, the price fluctuation of isobutanol during the same period was relatively small. During this period, the price trends of the two were highly consistent, and isobutanol also showed a trend of rising first and then falling. The highest point appeared in 2021, at 14600 yuan/ton; the lowest point appeared in 2025, at 7050 yuan/ton. During the recent period of price decline, the decline in the isobutanol market was smaller than that of n-butanol, which is the direct reason for the change in the price difference between the two and the fact that isobutanol surpassed n-butanol.
Stable supply structure and effective supply shrinkage are the key reasons for the relatively small price drop of isobutanol.
Compared with the continuous expansion of supply and demand and increasing oversupply of n-butanol in recent years, there are significant differences in the supply and demand structure of isobutanol. Overall, the supply structure of isobutanol has not changed much in recent years, but the actual supply has shrunk significantly. Although demand has declined during the same period, the degree of product oversupply is not large, which is one of the reasons why the price of isobutanol has fallen relatively slowly.
The monthly supply of isobutanol has decreased significantly in recent years. From a five-year comparison, the total monthly supply of isobutanol has decreased from 17,500 tons in 2021 to 12,500 tons recently, a decrease of 29%. Among them, production and imports have decreased simultaneously. First, let's look at production. The monthly production of isobutanol has decreased from 10,000-12,000 tons in 2021 to 6,000-10,000 tons in 2024-2025, a decrease of 20-30%; during the same period, imports have also decreased significantly, with monthly imports decreasing from 6.7K in 2021 to 3.9K currently, a decrease of 42%.
Combining the characteristics of the slow decline in isobutanol prices since 2024, the product has maintained a tight balance during this period, which is closely related to two factors. First, there are no new isobutanol plants put into operation during this period. Although the number of newly put into operation butanol plants has increased in recent years, they all produce isobutyraldehyde as a by-product, and no isobutanol production capacity has been put into operation; second, the price of isobutyraldehyde was higher than that of isobutanol in the early stage, which caused the switchable plants to produce more isobutyraldehyde and reduce the production of isobutanol. Since the second half of 2024, with the price advantage of isobutanol becoming apparent, the proportion of switchable plants producing isobutanol has increased, but it is still significantly less than isobutyraldehyde. Since the second quarter of 2025, the price of isobutyraldehyde has fallen rapidly, forcing switchable plants to produce isobutanol. As of May 20, three plants, including Nanjing Chengzhi, Tianjin Bohai Chemical Yongli, and Luxi Chemical, have switched to producing isobutanol, but due to the shutdown of the CNOOC Shell plant (from the end of March to the end of May), the overall supply pressure is not large, and the price remains high.
Future new production capacity will not be large, but effective production capacity will increase significantly, and the price difference between isobutanol and n-butanol is expected to quickly return to normal.
From the statistics of planned isobutanol plants under construction, only the Ningxia plant will resume production of isobutanol, but the capacity is relatively small. Because there are many planned butanol plants under construction in the future, most of them will resume production of isobutyraldehyde, the future oversupply of isobutanol will increase, which will inevitably force the existing isobutanol in the existing plants. /The switchable plants of isobutyraldehyde will significantly increase the production of isobutanol. According to statistics, the current capacity utilization rate of isobutanol plants is only around 30%, and the potential increase in future production is very significant. This means that after the oversupply of isobutyraldehyde accelerates, its impact on the extension of isobutanol will accelerate the increase in isobutanol production capacity. Considering the small scale of current isobutanol supply and demand, after the supply-side production capacity is restored, there is an expectation of rapid repair of the price difference between isobutanol and n-butanol.
Source: Zhuochuang Information

